Content

Other products that use any of these activities will also be assigned some of their costs. Product 366 will not be assigned any cost of special engineering or special testing, and it will be assigned what is activity based costing only a small amount of machine setup. Instead of using broad arbitrary percentages to allocate costs, ABC seeks to identify cause and effect relationships to objectively assign costs.
What is activity-based costing and its importance?
It's a process of tracking resource use and pricing final outputs. The goal of activity-based costing is to assign specific resources to objects. It specifically identifies the activities that cause production costs to increase, helping team leaders make more informed pricing and manufacturing strategies.
The traditional methods applied for absorbing overheads lay emphasis on the calculation and application of overhead recovery rates which are acceptable for the valuation of stocks for the purposes of routine financial reporting. The management is not able to find these different traditional methods of costing that may be helpful in making some hard decisions which may affect the product strategies. Under Conventional or Traditional Costing System, overhead expenses are identified initially with the cost centres which comprise of both the production departments and service departments. The costs of service departments are then distributed, on some equitable bases, to the production departments.
Difference between Traditional Costing and ABC Approach
The classical scenario we see here is trying to work out the cost of producing products. ABC as an approach was initially put forward by the Consortium for Advanced Management International, and was then developed by academics in the 1970s and 1980s.
- Our mission is to provide an online platform to help students to discuss anything and everything about Economics.
- For example, the cost of the activity of bank tellers can be ascribed to each product by measuring how long each product’s transactions take at the counter and then by measuring the number of each type of transaction.
- If we consider manufacturing businesses and how they’ve changed, the modern manufacturing environment is much different compared to the traditional manufacturing environment.
- Let’s look at how these steps might work when evaluating the cost of bank loans.
- The factors which influence the cost of a particular activity should identified, which are known as Cost Drivers.
Duration drivers establish an average hourly rate of performing an activity while intensity drivers involve direct charging based on the actual activity resources relevant to a product. There has been an increase in tendency towards product diversification to secure economies of scope and increased market share requiring the ascertainment of more accurate product costs under the conditions of fast changing cost structure. The traditional absorption costing does not render any valuable assistance to multi-product concerns in making decisions regarding process technology, product-mix, product pricing etc. It charges overhead cost to product according to activities involved in the product instead of using average overhead distribution rate as in case of traditional method. Thus, in ABC, overhead cost is attributed to the cost centre or unit on the basis of number of activities undertaken in production.
Asia Pacific Management Review
For example, if the customer service department gets a new database system, the reps may be able to perform a standard credit check in 20 minutes rather than 50 minutes. To accommodate the improvement, just change the unit time estimate to 20 minutes, and the new cost-driver rate automatically becomes $16 per https://www.bookstime.com/ credit check (down from $40). Of course, you then have to add back in the cost impact of purchasing the new database system by updating the cost per time unit estimate, so the final figure may be somewhat higher than $16. ABC focuses attention on cost drivers, the activities that cause costs to increase.
- But while that distribution did reflect how workers spent their productive time, the fact that their total productive time was significantly less than their practical capacity of 32 hours per worker per week was completely ignored.
- For example, the capacity of a warehouse or vehicle would be measured by space provided, while memory storage would be measured by megabytes supplied.
- The first step in ABC is to identify the major activities which take place in an organisation.
- So, a nice simple cost driver for activity one , might be the number of supply orders, because every time we have to place an order, while we have a procurement team who would be responsible for that, we’re using resources.
- Activity-based costing is an accounting method that assigns costs to the different activities involved in making a product in order to allocate a company’s funds in a fair way.
- However, since it is costly to gather the data for analysis it is usually only beneficial for larger companies with high overhead costs to use an activity-based costing system.
Then these costs are assigned and the manner in which the final bearer of each cost has consumed the services of each activity determines how these costs are allocated. In a service environment, the allocation of costs to service delivery may not be easy.
ABC – Definition
Inductors of intensity, which measure resource consumption every time an activity is performed. A cost element refers to an account which receives and accumulates costs over a period of time. It also includes the revenue accounts that receive and accumulate revenues over a period of time. In addition to this, this system makes it possible to make assertive decisions with assurance in terms of pricing and the analysis and control of products, markets, channels, clients, etc. With your application and report analysis, your system can evolve, which will affect the effective tracing of more and more of your company’s activities. In this way, even if certain expenses are grouped within the same cost center, they’ll be organized according to the activity to which they’re linked.
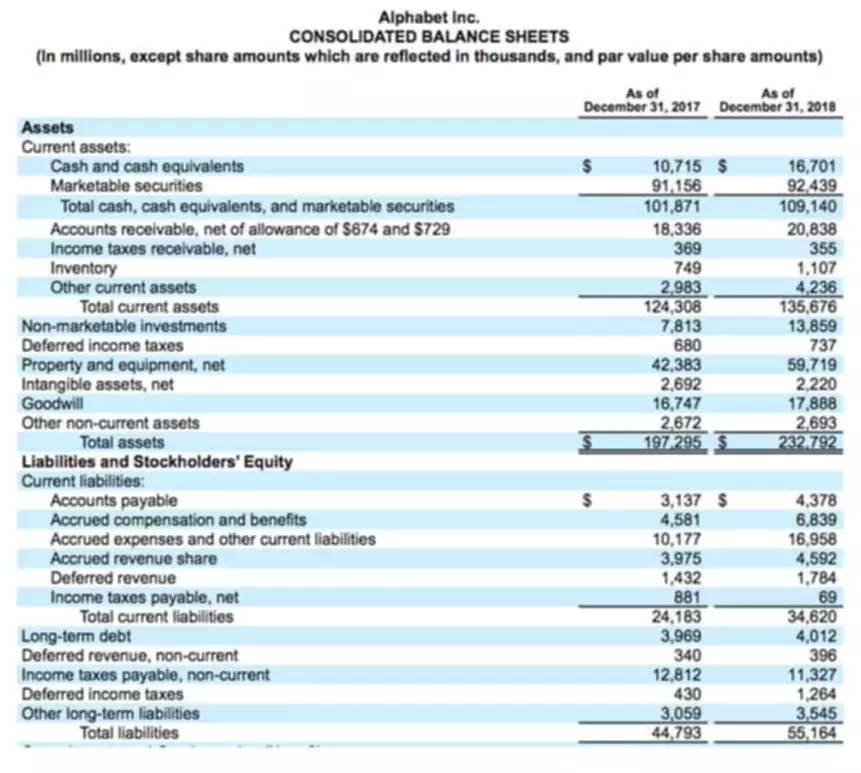
Activities consume overhead resources and are considered cost objects. Activity-based costing is a method of assigning overhead and indirect costs—such as salaries and utilities—to products and services. Delivering high-quality, cost-efficient care to specific patient populations within a service line is nearly impossible without a sophisticated costing methodology. With traditional costing, there is only one company/plant-wide overhead rate.
What Are the Benefits of Activity-Based Costing?
The purchase requisition note is not raised in the purchasing department where most of the costs relating to procurement or purchase are incurred. Activity costs tend to behave in a similar manner to each other i.e., they have the same cost driver or the factor causing a change in the cost of an activity. Thus, it is believed that activity-based costing helps in presenting a more realistic picture of the behavior of costs. Within this context, MyABCM’s software has been developed to provide management based on activities, favoring cost control and your business’s return on investment. The description of the specifics of each process and its costs makes a multidimensional analysis with a panoramic focus on the costs of each activity possible. In this way, greater than expected costs can be identified and the budget can even be revised to eliminate expenses that are revealed to be greater than necessary.
- Or machine hours, it will create new bases to assign these overhead costs to items upon these activities, which shall generate costs.
- Identifying cost drivers requires gathering information and interviewing key personnel in various areas of the organization, such as purchasing, production, quality control, and accounting.
- Examples of cost drivers include machine setups, maintenance requests, consumed power, purchase orders, quality inspections, or production orders.
- Additionally, one of the newer tools is the orchestrator which is very good.
- Cost drivers are most often used in the allocation of cost pools to cost objects.
- Once the model is defined it’s time to perform the calculation, generate simple and complex data cubes , and create simple and advanced what if scenarios.
These levels include batch-level activity, unit-level activity, customer-level activity, organization-sustaining activity, and product-level activity. In the case of our customer service department, the traditional ABC survey produced a work distribution of 70%, 10%, and 20% of the employees’ time performing the department’s three activities. But while that distribution did reflect how workers spent their productive time, the fact that their total productive time was significantly less than their practical capacity of 32 hours per worker per week was completely ignored. For example, a chair manufacturer manufactures two products, a standard chair and a custom chair, and estimates manufacturing overhead costs of $1,000,000.
